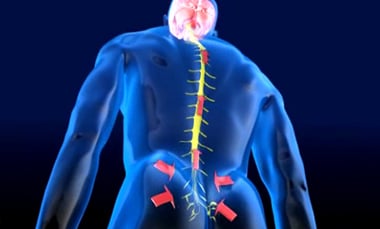
Spinal cord stimulators (SCS) are electronic devices designed to reduce chronic pain in patients with spinal cord injuries, fused vertebrae, damaged discs, and other back injuries. The spinal cord and brain communicate with each other to transmit signals of pressure, sensation, and pain. When back injury patient feels pain, it’s because the nerve fibers in the spine send a pain signal to your brain.
Spinal cord stimulators can be a means of managing pain without drugs by interrupting or “masking” pain signals before they reach the brain. Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) works by masking these signals. With SCS therapy, a small implantable pulse generator (or IPG) and thin wires (leads) are placed in the body. The leads then deliver tiny pulses to the nerves that mask pain signals as they travel to the brain, producing a tingling sensation, which reduces the feeling of pain. Physicians refer to the effect as “paresthesia.”
Advantages of Spinal Cord Stimulators
There are several advantages to spinal cord stimulation, also known as peripheral nerve field stimulation, for the treatment of chronic back pain in those with back and spinal cord injuries:
- A trial period may test patient response before the patient commits to a permanent surgical implant.
- An implant has few side effects and is easily reversible; if it doesn’t work or is no longer needed it can be removed.
- Implantation of the system is minimally invasive, requiring a relatively minor surgical procedure on an outpatient basis.
- Electric leads are inserted just under the skin, and patients can travel anywhere and participate in any type of normal activities, including swimming.
- Achieving pain relief with spinal cord stimulation or peripheral nerve field stimulation can allow patients to reduce or eliminate any risk of dependency on narcotic drugs.
- Ongoing advances in neurostimulator technology offers patients better control over adjustments to the stimulation if their pain changes in location or severity.
Disadvantages of Spinal Cord Stimulators
As with any chronic pain treatment, there are also a few notable disadvantages with spinal cord stimulation, including:
- Spinal cord stimulation does not work for every patient. Most studies show that 50% – 60% of people find meaningful pain relief with spinal cord stimulation.
- SCS does not entirely eliminate the pain. A successful outcome of spinal cord stimulation is considered to be pain relief of 50% or more.
- Spinal cord stimulation does not address the source of the pain. The system is designed to interrupt pain signals being sent to the brain, but it does not correct any underlying anatomical issue causing the pain. For many people with chronic pain, this is the right approach to treatment. However, for those with a correctable anatomic lesion, treatments to address the source of the pain should be tried first.
- SCS treatment involves an implant and surgery. There are certain basic risks with any surgical procedure and implant.
Risks Factors Involving Spinal Cord Stimulation
Spinal cord stimulation and peripheral nerve field stimulation expand the range of treatment options for patients experiencing chronic pain. Patients with chronic pain should consult with their physicians to discuss whether stimulation therapy could be right for them given their medical history.
As with all surgical procedures, there are potential risks to stimulation therapy, although most are relatively minor. Risks include:
- Allergic reaction to the implanted materials
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Migration of the electrode may occur, resulting in a loss or change of stimulation
- Skin breakdown over the generator or electrode site
- Stimulation may work for a period of time and then lose effectiveness after 1-2 years
- Pain at the incision site (usually resolves in a few weeks)
- Weakness, numbness, clumsiness, paralysis
- Battery failure and/or battery leakage requiring a surgical incision to remove and replace the battery
- Fluid leakage from the spinal cord, causing headaches
- Undesirable changes in stimulation can develop over time due to scar tissue forming around the leads, or movement of the lead position
- Undesirable or unpleasant stimulation affecting the chest or rib area as a result of nerve root involvement
References:
Boston Scientific